Urticaria: Causes and Treatment
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a common skin condition that affects up to 20% of people at some point in their lives. It is characterized by itchy, red, and swollen welts on the skin that can appear suddenly and disappear within hours or days.
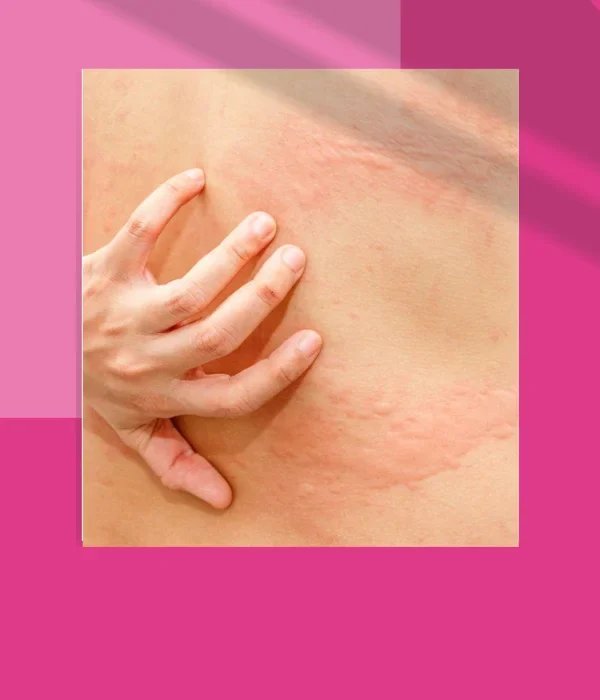
Urticaria is a skin condition that causes red, itchy, and swollen welts on the skin. These welts can appear on any part of the body, and they can vary in size and shape. Urticaria is also known as hives or nettle rash.
Urticaria is a common condition, and it can affect people of all ages and races. The condition can last for a few hours to several days and can be very uncomfortable.
There are several types of urticaria, including acute urticaria, chronic urticaria, physical urticaria, dermatographic urticaria, and cholinergic urticaria.
Acute Urticaria
Acute urticaria is a short-term condition that usually lasts for a few hours to a few days. It is often caused by an allergic reaction to food, medication, or insect bites.
Chronic Urticaria
Chronic urticaria is a long-term condition that lasts for more than six weeks. The cause of chronic urticaria is often unknown, but it is believed to be related to an autoimmune disorder.
Physical Urticaria
Physical urticaria is caused by physical stimuli such as heat, cold, pressure, or exercise. This type of urticaria can be triggered by exposure to hot water, sunlight, or even by scratching the skin.
Dermatographic Urticaria
Dermatographic urticaria, also known as skin writing, is a type of urticaria where the skin becomes red and swollen when it is rubbed or scratched.
Cholinergic Urticaria
Cholinergic urticaria is a type of urticaria that is caused by an increase in body temperature. This can be triggered by exercise, emotional stress, or even eating spicy foods.
The exact cause of urticaria is often unknown, but it can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
Allergies
Urticaria can be caused by an allergic reaction to certain foods, medications, or insect bites. Common food allergens that can trigger urticaria include peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, and dairy products. Some medications that can cause urticaria include antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and aspirin.
Infections
In some cases, urticaria can be caused by an infection such as a viral or bacterial infection. This is known as viral urticaria or bacterial urticaria.
Medications
Certain medications can cause urticaria as a side effect. This includes antibiotics, pain relievers, blood pressure medications, and sedatives.
Stress
Stress can trigger urticaria in some people, as it can cause the body to release histamine, a chemical that can cause the skin to become red, itchy, and swollen.
Food additives
Some food additives, such as preservatives and artificial colors, can trigger urticaria in some people.
The symptoms of urticaria can vary from person to person, but they typically include:
- Red, itchy, and swollen welts on the skin
- The welts can appear on any part of the body and can vary in size and shape
- The welts can come and go quickly, sometimes within minutes or hours
In some cases, urticaria can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as:
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat
- Difficulty breathing
- Dizziness or fainting
To diagnose urticaria, a doctor will typically take a medical history and perform a physical examination. They may also perform certain tests to rule out other conditions.
Medical History and Physical Examination
During a medical history, the doctor will ask about your symptoms, when they started, and what seems to trigger them. They may also ask about your medical history and any medications you are taking.
During a physical examination, the doctor will look for any signs of urticaria on your skin.
Skin Tests
Skin tests, such as a skin prick test or a patch test, can be used to determine if you have an allergy that is causing your urticaria.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can be used to check for specific antibodies that can indicate an allergy.
The treatment of urticaria depends on the severity and duration of the condition. In many cases, urticaria will go away on its own within a few hours or days. However, if the symptoms are severe or persistent, treatment may be necessary.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are typically the first line of treatment for urticaria. They work by blocking the effects of histamine, which can reduce itching and swelling. Antihistamines are available over-the-counter and in prescription strength.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids can be used to reduce inflammation and swelling in severe cases of urticaria. However, they should only be used for a short period of time, as long-term use can have serious side effects.
Immunosuppressants
In rare cases, immunosuppressant medications may be used to treat chronic urticaria. These medications work by suppressing the immune system, which can help to reduce inflammation and itching.
Other Medications
Other medications that may be used to treat urticaria include leukotriene inhibitors, which can block the effects of certain chemicals that cause inflammation, and omalizumab, which is a biologic medication that can help to prevent the release of histamine.
Avoiding Triggers
In some cases, avoiding the trigger that is causing the urticaria may be enough to prevent symptoms from occurring. This may involve avoiding certain foods or medications, or taking steps to reduce stress.
There are several steps that you can take to help prevent urticaria, including:
- Avoiding known triggers, such as certain foods or medications
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga
- Avoiding tight-fitting clothing that can irritate the skin
- Using fragrance-free and dye-free products on the skin
- Keeping the skin well-moisturized
Is urticaria contagious?
No, urticaria is not contagious.
Can urticaria be cured?
While there is no cure for urticaria, symptoms can be managed with medications and by avoiding triggers.
How long does urticaria last?
Urticaria can last anywhere from a few hours to several weeks, depending on the cause and severity of the condition.
Can stress cause urticaria?
Yes, stress can trigger urticaria in some people.
Can urticaria be life-threatening?
In rare cases, severe urticaria can cause a life-threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. If you experience symptoms such as swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, or dizziness, seek emergency medical attention.
When choosing a skin clinic for urticaria treatment, it’s important to consider the following factors:
Experience and expertise: Veeha Skin Clinic has experienced and knowledgeable dermatologists, who specialize in treating urticaria.
Treatment options: We offers a variety of treatment options, such as topical medications, oral medications, so that you can find the best treatment for your individual needs.
Personalized treatment plans: We work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your individual needs and concerns.
Quality of care: We have prioritizes patient safety with evidence-based treatments.
Reputation and reviews: We have good reputation and positive reviews from previous patients.
Location and Accessibility: We have well-located and accessible clinic so you can easily attend appointments and receive ongoing treatment as needed.
By considering these factors, you can choose Veeha Skin Clinic for urticaria treatment that best suit your individual needs and offers you effective and personalized urticaria treatment.
Book Now
Make An Appointment
Consult with Rajkot leading Dermatologist & Cosmetologist, Dr. Pratik Siddhapura M.D Skin. He has many years of experience in treating urticaria patients, he will evaluate your individual skin condition and discuss the treatment options with you. You may also send an Online consultation request by contacting us : https://veehaskinclinic.com/contact-us/. Our team will respond to your questions or appointment request as soon as possible.
Opening Hours
- 09.30 AM - 02.30 PM
- 04.30 PM - 08.30 PM
- Closed
Support
You can contact us through phone, whatsapp & email. Online video consultations are also available.

